vold share 操作清理正在使用磁盘的进程分析
更新日期:
vold 是 android system/bin 下的一个本地程序(代码在 system/vold 下)。用于处理 framework 中各种和 mount、unmount 相关的命令。 vold 的框架结构分析,推荐去看一本叫《深入理解 Android 卷I》的第九章,很详细。不过这本书在最后留了个问题,就是当把磁盘挂在到 PC 上(这个就是 vold 的 share 操作)的时候会导致一些进程被杀掉。正好UP主的这段时间的工作也和这个有关,这里在主要是解答下这个小问题。不过首先废话下 android 的2种 usb 模式:
2种 usb 模式
首先说下 android 上目前支持的2种 usb 连接模式:
UMS(USB Mass Storage)
这种模式下,会将 android 的磁盘从系统中 umount 出去,然后 mount 到 PC 上,就和 PC 上插上U盘类似。使用这种模式,由于需要把 umount 磁盘,所以在使用过程中,android 系统无法使用磁盘。 vold 就是这种模式下用的。MTP(Media Transfer Protocol)
媒体传输协议(具体的百度、google 去吧)。和 UMS 最大的不同,就是不需要 umount 磁盘,插上 PC 后,就和插入数码相机类似,可以查看、copy 多媒体文件到磁盘中。所以这种模式下,android 系统是能够继续使用磁盘的。但是也存在缺点:只能管理多媒体文件,文件IO 速度和稳定性比 UMS 稍差。原生 android 从 4.0 之后默认使用这种模式。
访问磁盘的进程检测
在 UMS 下,连接 usb , 打开 SystemUI 的 UsbStorageActivity,点击 mount 按钮,会在 checkStorageUsersAsync() 会调用 MountService 的 getStorageUsers() 去检测有哪些进程还在访问磁盘:
|
|
MountService 里面的 getStorageUsers() 会调用 NativeDaemonConnector 的 executeForList() 方法:
|
|
NativeDaemonConnector 是 MountService 用来和 Vold 通讯用的。java 层通过 Unix socket 和 native vold 进行通讯(遵守 android 自己定义的通讯协议,暂时不清楚为声明不用 binder)。exectueForList() 最后调用自己内部的 exectue() 把一个 “storage” 命令 + 检测路径(path)打包转化为协议数据包二进制流,然后通过写到 socket 里面:
|
|
在 vold 这边, CommandListener 有一个对应 “storage” 命令的处理实现 StorageCmd 。这个实现会用 Process 的 checkFileDescriptorSymLinks() 去检测是否用进程在访问磁盘。检测的方法是:去 /proc/xx/ 下(xx 是进程号 pid,每个打开了 fd 的进程会在系统的 /proc 下有记录的)检测3种东西:
checkFileDescriptorSymLinks
这个是检测进程打开的 fd 的链接路径(Process 通过 linux 系统函数 readlink 去获取一个 fd 的真实文件物理路径,例如 /proc/2100/40 可能的真实 link 是 /mnt/sdcard/text.txt)是否和传入的 mountPoint 一致(一般这就是 sdcard 的挂载点路径,由 java 层传入。不过偶尔也会有坑,例如某些 rom sdcard 挂载点,为了兼容性,弄了一个文件链接给应用用,导致应用打开的 fd 路径和 mount 的时候检测的路径字符串不一样,注意是字符串不一样,导致检测不到进程在访问 sdcard),如果一致就表示该进程正在访问磁盘。checkFileMaps
这个是检测 /proc/xx/maps ,这个我暂时不知道声明情况下会有记录。checkSymLink
这个是检测 /proc/xx/cwd、/proc/xx/root、/proc/xx/exe ,这个目的应该是判断应用时候安装在 sdcard 上,或是有使用的数据在 sdcard 上(例如一些大型游戏的 data 数据)。如果是安装在 sdcard 上的应用,mount 出去的时候肯定要停止才行。
如果上面3种检测任何一种检测到了(返回值为 1),就给 stocket 写该进程的 pid 号,这样 java 层就知道有哪些进程在访问磁盘了。UsbStorageActivity 那里的表现就是弹出一个确定对话框告诉用户现在还有程序在访问磁盘,如果挂载 usb 设备则这些应用可能会出现异常(其实就是要强制杀死它们而已)。如果用户点确定,MountService 在开启 UMS 之前会让 ActivityManager 把那些还在访问磁盘的进程杀掉。先上剩余坚持代码:
|
|
说那么多,上个图先: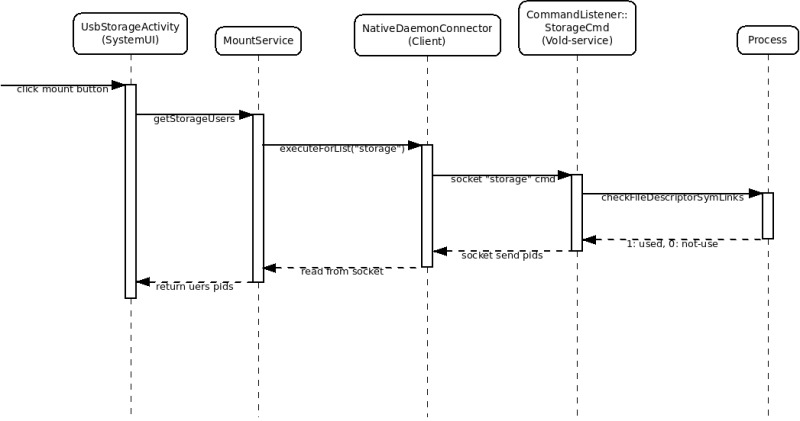
杀死访问磁盘的进程
上面分析在点击挂载到 PC 的时候,如果检测到有进程在访问磁盘,则会弹个询问框出来,告诉用户现在有程序在访问磁盘,如果还是要挂载磁盘则这些程序可能会出现异常。如果点击确定就会先调用 StroageManager 的 enableUsbMassStorage(),这个最后会调用 MountService 的 setUsbMassStorageEnabled(true) 去向 vold 发 shared 命令去把磁盘从 android 中 unmounted,然后再 shared 到 PC 上。
(具体过程以后再分析)
其中 package manager 会收一些广播,然后干一些磁盘 umount 相关的事情,干完后,pm 会调用 MountService 的 finishMediaUpdate() 通知 MountService,然后在 MountService 自己的 Handler 中处理这个消息时候就会调用 ActivityManager 的 killPids 去杀死这些还在访问的磁盘的进程,让挂载能够顺利的进行下去。
Package Manager 中的 Handler 处理:
|
|
MountService 中的处理:
|
|